WTF Solidity: 22. Call
Twitter: @0xAA_Science | @WTFAcademy_
Community: Discord|Wechat|Website wtf.academy
Codes and tutorials are open source on GitHub: github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity
Previously in 20: Sending ETH we talked about sending ETH with call, in this tutorial we will dive into that.
Call
call is one of the address low-level functions which is used to interact with other contract. It returns the success condition and the returned data: (bool, data).
- Officially recommended by
solidity,callis used to sendETHby triggeringfallbackorreceivefunctions. callis not recommended for interacting with other contract, because you give away the control when calling a malicious contract. The recommended way is to create a contract reference and call its functions. See 21: Interact with other Contract- If the source code or
ABIis not available, we cannot create contract variable; However we can still interact with other contract usingcallfunction.
Rules of using call
Rules of using call:
targetContractAddress.call(binary code);
the binary code is generated by abi.encodeWithSignature:
abi.encodeWithSignature("function signature", parameters separated by comma)
function signature is "functionName(parameters separated by comma)". For example, abi.encodeWithSignature("f(uint256,address)", _x, _addr)。
In addition, we can specify the value of ETH and gas for the transaction when using call:
contractAdress.call{value:ETH value, gas:gas limit}(binary code);
It looks a bit complicated, lets see how to use call in examples.
Target contract
Lets write and deploy a simple target contract OtherContract, the code is mostly same as chapter 19, only with an extra fallback function。
contract OtherContract {
uint256 private _x = 0; // state variable x
// Receiving ETH event, log the amount and gas
event Log(uint amount, uint gas);
fallback() external payable{}
// get the balance of the contract
function getBalance() view public returns(uint) {
return address(this).balance;
}
// set the value of _x, as well as receiving ETH (payable)
function setX(uint256 x) external payable{
_x = x;
// emit Log event when receiving ETH
if(msg.value > 0){
emit Log(msg.value, gasleft());
}
}
// read the value of x
function getX() external view returns(uint x){
x = _x;
}
}
This contract includes a state variable x, a Log event for receiving ETH, and three functions:
getBalance(): get the balance of contractsetX():external payablefunction, can be used to set the value ofxand receivingETH.getX(): get the value ofx.
Contract interaction using call
1. Response Event
Lets write a Call contract to interact with the target functions in OtherContract. First we declare the Response event, which takes success and data returned from call as parameters. So we can check the return values.
// Declare Response event, with parameters success and data
event Response(bool success, bytes data);
2. Call setX function
Now we declare the callSetX function to call the target function setX() in OtherContract. Meanwhile we send msg.value of ETH, then emit the Response event, with success and data as parameter:
function callSetX(address payable _addr, uint256 x) public payable {
// call setX(),and send ETH
(bool success, bytes memory data) = _addr.call{value: msg.value}(
abi.encodeWithSignature("setX(uint256)", x)
);
emit Response(success, data); //emit event
}
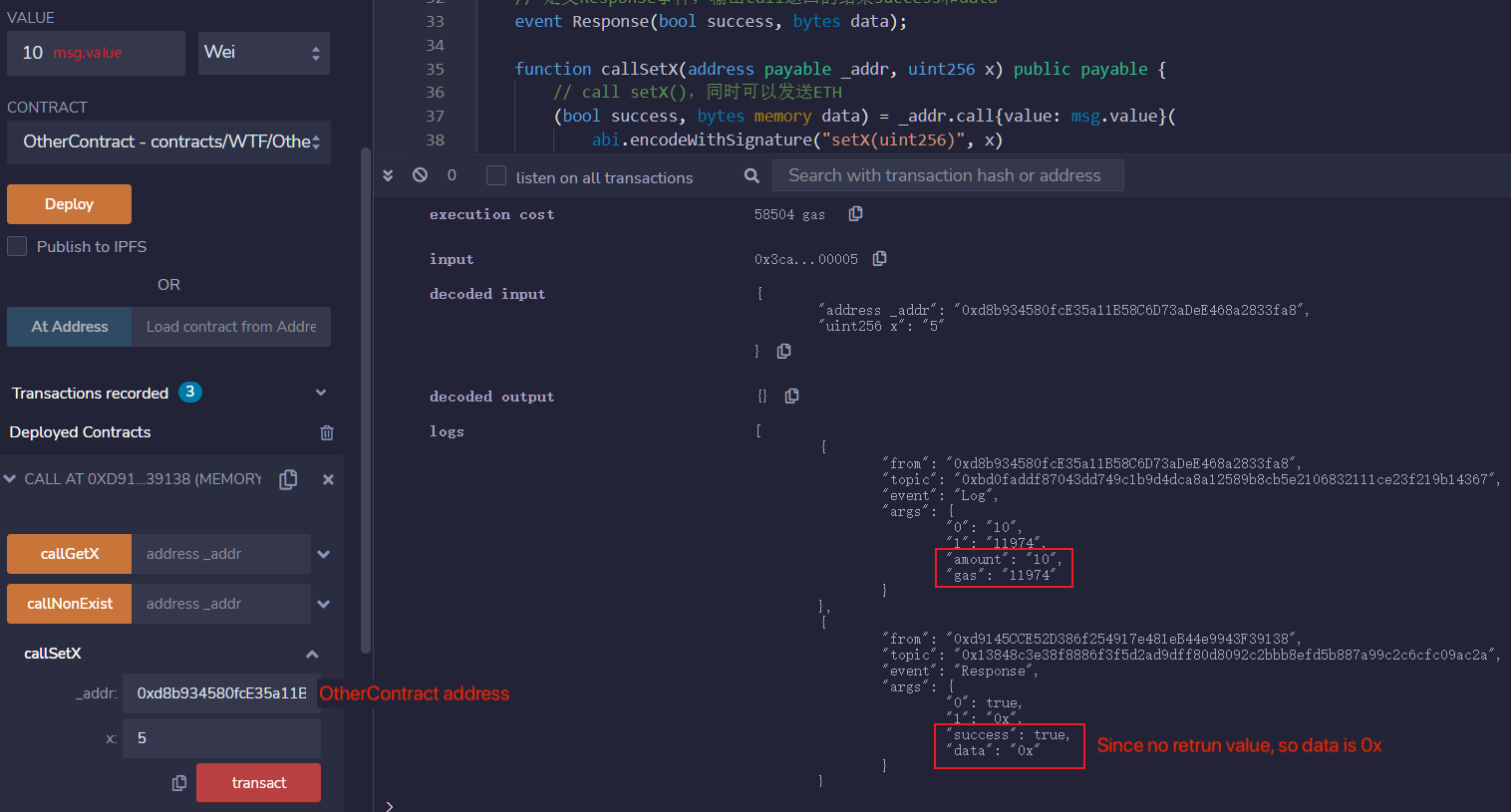
Now we call callSetX to change state variable _x to 5, pass the OtherContract address and 5 as parameters, since setX() does not have return value, so data is 0x (i.e. Null) in Response event.
3. Call getX function
Next we call getX() function, it will return the value of _x in OtherContract, the type is uint256. We can decode the return value from call function, and get its value.
function callGetX(address _addr) external returns(uint256){
// call getX()
(bool success, bytes memory data) = _addr.call(
abi.encodeWithSignature("getX()")
);
emit Response(success, data); //emit event
return abi.decode(data, (uint256));
}
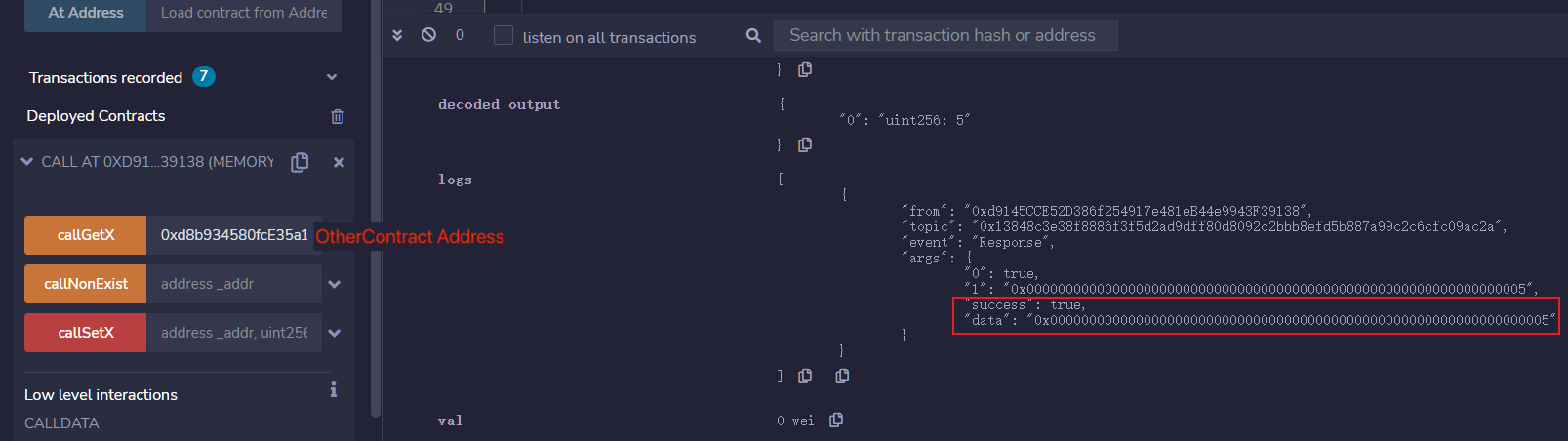
From the log of Response event, we see data is 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005. After decoding with abi.decode, the final return value is 5.
4. Call undeclared function
If we try to call functions that are not present in OtherContract with call, the fallback function will be executed.
function callNonExist(address _addr) external{
// call getX()
(bool success, bytes memory data) = _addr.call(
abi.encodeWithSignature("foo(uint256)")
);
emit Response(success, data); //emit event
}
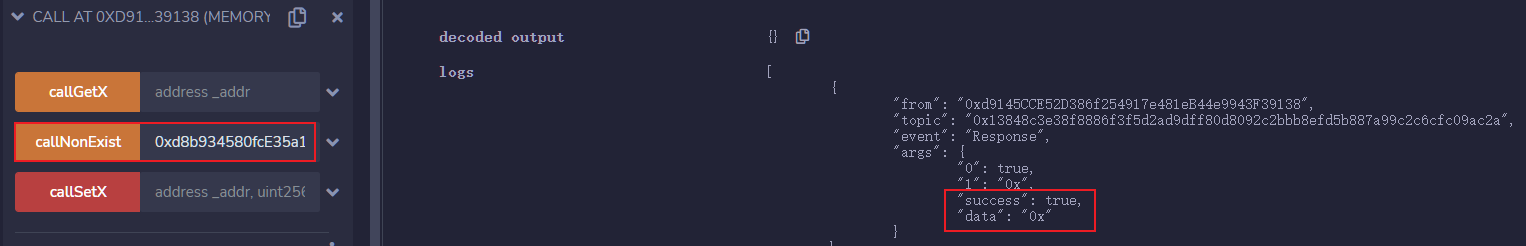
In this example, we try to call foo which is not declared with call, the transaction will still succeed and return success, but the actual function executed was the fallback function.
Summary
In this tutorial, we talked about how to interact with other contract using low-level function call. For security reasons, call is not recommended method, but it's useful when we don't know the source code and ABI of the target contract.